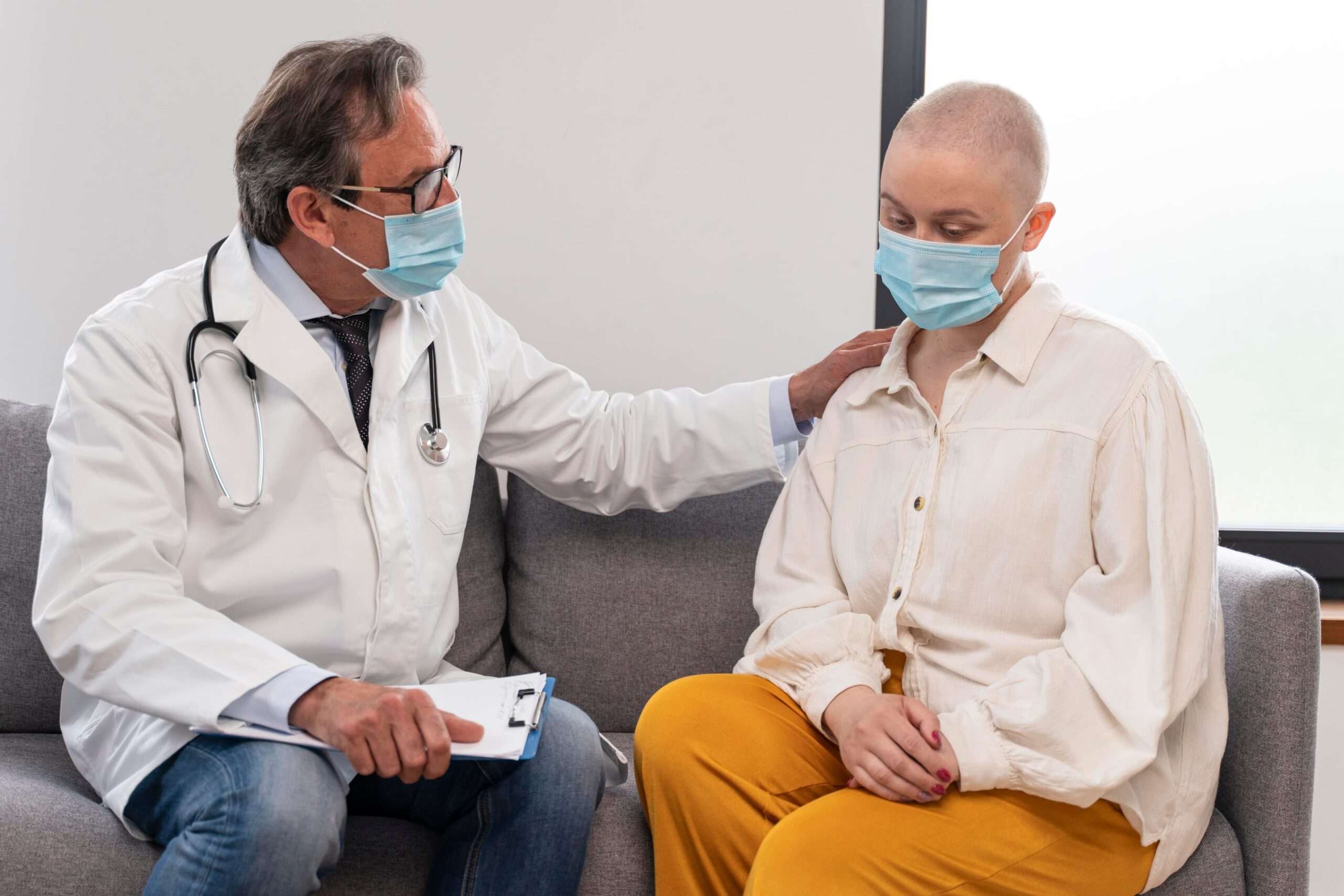
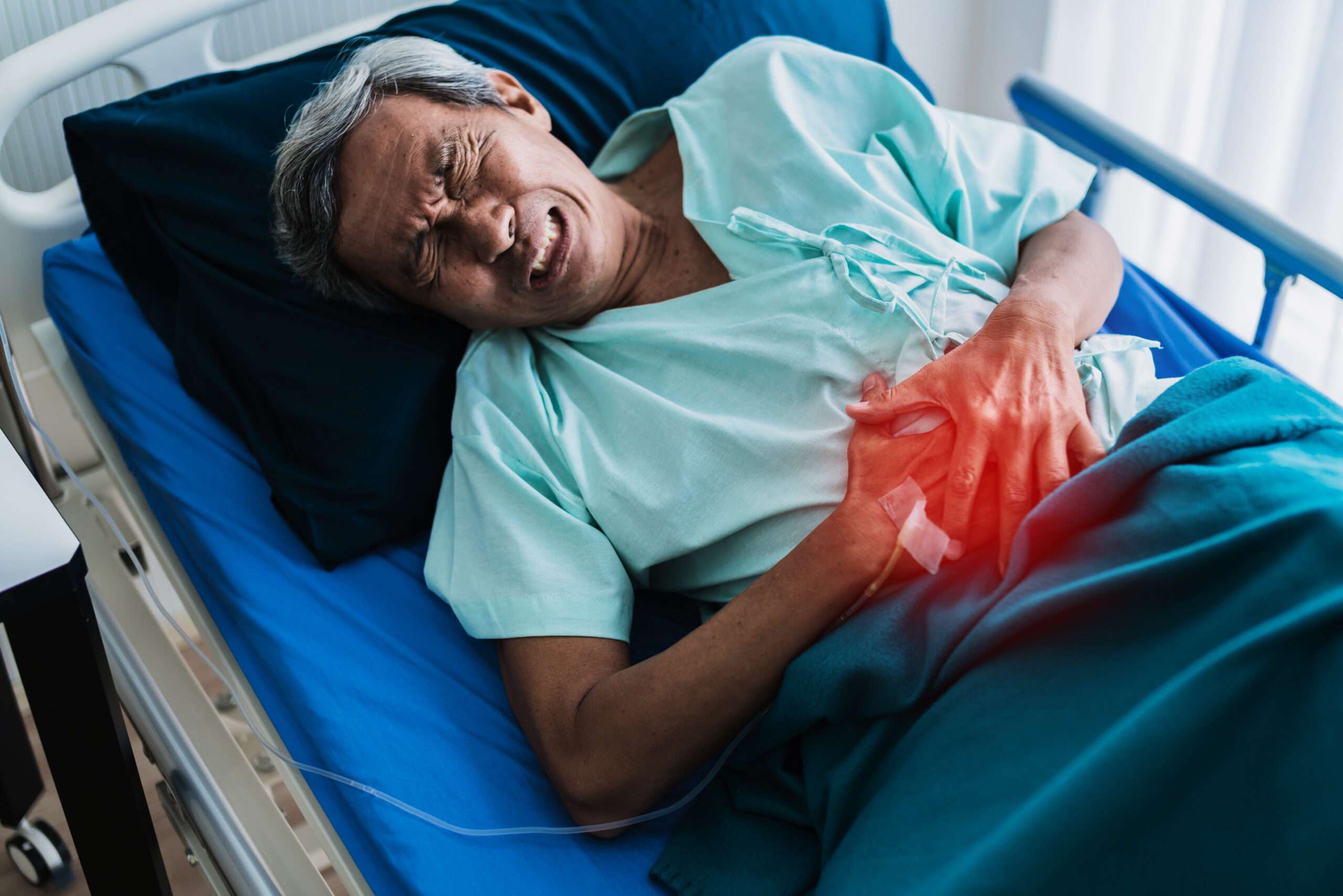
The SPIKES protocol is a strategy to break bad news effectively and communicate with the person or people involved with empathy and professionalism.
It is primarily developed for healthcare settings to help healthcare professionals break bad news to patients and their families effectively.
Bad news is any news or information that changes a person’s view of the future in a negative way.
For example, delivering the news to a patient that his test report shows a terminal condition like cancer, telling a patient that he has a chronic disease like diabetes or high blood pressure, or telling the relatives of the patient that the patient is no more because of treatment failure, etc.
These types of news are very challenging for healthcare professionals and need a structured approach to follow. Here, you not just transfer the information, which will change the patient’s view of the future, but at the same time deal with the emotions of patients and their relatives and also give them the future strategy to follow.
In this blog post, we will learn what the SPIKES protocol, is, where we can apply it, and why it is so effective for healthcare professionals.
What is SPIKES?
The word SPIKES stands for
- S: Setting up the Interview
- P: Patient’s Perception
- I: Patient’s Invitation
- K: Giving information or knowledge to patients
- E: Emotions or Empathy
- S: Strategy or Summary
Step-by-step breakdown of the SPIKES protocol:
Setting up the interview
The healthcare professional should arrange a sitting with the patient and its relatives for the purpose of breaking bad news. The place should be quiet and private to minimize the interruption and make your communication more effective. Always make sure that the patient is accompanied by their relative or friend.
You just do not break bad news to a patient in a hospital corridor or in a busy clinic setting.
Perception
The next step in the SPIKES protocol is to know the patient’s understanding of the situation. A healthcare professional must build a rapport with the patient and ask them what he or she knows about the disease or the tests ordered and how it will affect the patient.
Invitation
Breaking bad news is not just passing information to the patient and their relatives. You first ask them if they really want to hear about the information. Don’t just break it without first knowing the patient’s invitation to hear it.
Knowledge
In this step, the healthcare professional passes the information or the bad news. The news delivered should be straight forward without any confusing statements or medical jargon that the patient does not understand.
It should be in small chunks, with the first warning them that you are going to share with them something not really good, to make the patient mentally prepare. then deliver some information and wait for a few moments to let the patient absorb it, and gradually you pass exact information.
Emotions or empathy
In this, you have to deal with the emotions of the patients and their relatives when the news is delivered; there a number of emotional reactions to it.
The healthcare professional must be aware of it and how to deal with those emotions with empathy. It could be complete silence with the patient becoming completely blank or denial from the patient side.
Summary or strategy
In this step, the healthcare professional recapitulates the steps with the patient, making sure he understands what has been delivered completely. Here you also give them a future strategy to follow, which is to give them a roadmap for what to do next.
Why SPIKES protocol Works
The reason why the SPIKES protocol works so effectively is because it provides a six-step approach toward breaking bad news. This structured approach makes it easy to deliver the bad news, deal with patients emotions with empathy, and give them future strategies.
Other alternatives to SPIKES PROTOCOL
The SPIKES protocol is not the only one to break bad news to the patient and their relatives. There are also other protocols certain approaches to do it in step wise manner
BREAKS protocol
B: background
R: rapport
E: explore
A: announce
K: kindle
S: summaize
ABCDE protocol
A: advance preparation
B: building a therapeutic environment
C: communication
D: dealing with reactions E: encouraging and validating the emotions
Conclusion
The SPIKES protocol is a structured, six-step approach primarly designed for healthcare professionals to deal with difficult situations effectively and with professionalism. You must follow these steps to improve your communication and deal with patients emotions with empathy.